Back pain is one among the foremost common reasons people attend the doctor or miss work, and it’s a number one explanation for disability worldwide. It may result from injury, activity, and a few medical conditions. Back pain can affect people of all ages, for different reasons. We are discussing on ICD 10 code for low back pain in this medical billing blog.
Pain in the lower back is very common today. The main reason for this is our wrong posture, getting up, sitting and working throughout the day. Low back pain can be caused by a strain in the back muscles or tendons. Other causes include arthritis, structural issues and disc injuries. The Low back pain often gets better with rest, physical therapy, and medication. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can help reduce the risk of low back pain.
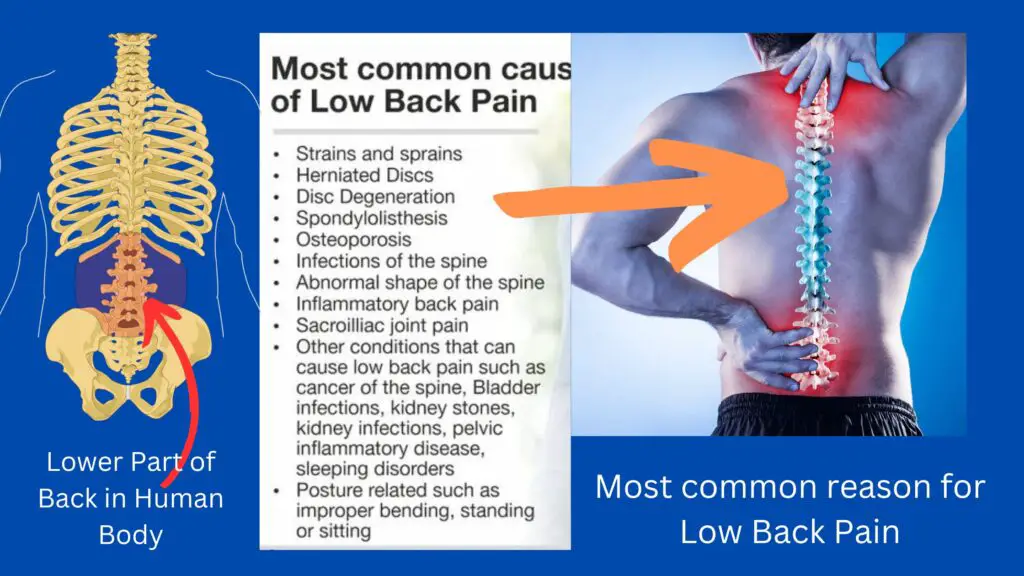
Lower back pain could also be linked to the bony lumbar spine, discs between the vertebrae, ligaments round the spine and discs, medulla spinalis and nerves, lower back muscles, abdominal and pelvic internal organs, and therefore the skin round the lumbar area.
Table of Contents
- ICD 10 Code for Chronic Low Back Pain
- What is low back pain?
- Reason for Low Back Pain
- Special Tests for Low Back Pain
- Low Back Pain Medication
- How it affect your daily life?
- Cause of Lower and Upper Back Pain
- Home Exercise for Backpain
- low back pain ICD 10
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion:
- Related Articles:
ICD 10 Code for Chronic Low Back Pain
Chronic low back pain is a common condition classified as M54.5 under the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10). It refers to a condition characterized by persistent low back pain, which usually lasts for at least 12 weeks or longer.
| ICD 10 Code for low back Pain | Code Description |
| M54.5 | Low back pain |
| M54.50 | Low back pain, multiple sites in spine |
| M54.55 | Low back pain, thoracolumbar region |
| M54.56 | Low back pain, lumbar region |
| M54.57 | Low back pain, lumbosacral region |
| M54.58 | Low back pain, sacral and sacrococcygeal region |
| M54.59 | Low back pain, site unspecified |
| M54.6 | Pain in thoracic spine |
| M54.8 | Other dorsalgia |
| M54.81 | Occipital neuralgia |
| M54.89 | Other dorsalgia |
| M54.9 | Dorsalgia, unspecified |
| M60 | Myositis |
| M60.0 | Infective myositis |
| M60.00 | Infective myositis, unspecified site |
| M60.000 | Infective myositis, unspecified right arm |
| M60.001 | Infective myositis, unspecified left arm |
What is low back pain?
Pain can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by stiffness, decreased range of motion, and difficulty with daily activities. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including old age, injury, or degenerative changes in the spine. Treatment options for chronic low back pain include physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgery.
Low back pain is a common condition that affects the lower part of the spine, particularly the lumbar region. Pain can range from mild to severe and, in some cases, it can make it difficult or impossible to perform daily activities such as walking, sitting, or sleeping. This can be caused by a wide range of factors, including poor posture, muscle tension, injury, or underlying medical conditions such as arthritis or disc herniation.
Generally, low back pain can be relieved with rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy (PT). Cortisone injections and hands-on treatments (such as osteopathic or chiropractic manipulation) can provide relief from pain and aid in the healing process.
Reason for Low Back Pain
Low Back pain is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including:-
● Poor sitting posture or ergonomics, which can put excessive stress on the muscles and ligaments of the lower back.
● Pulling or spraining muscles due to lifting heavy objects or sudden movements.
● Herniated or bulging disc, which can compress nerves and cause pain.
● Osteoarthritis or other degenerative joint conditions.
● Spinal stenosis, which is a narrowing of the spinal canal.
● Scoliosis, an abnormal curvature of the spine.
● Osteoporosis, a condition in which bones become weak and brittle.
● Inflammatory conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Special Tests for Low Back Pain
Low back pain is a common health condition that can have many causes. There are a number of tests that can be used to help diagnose the cause of low back pain. Here are some of the most common tests:-
● Straight leg raise test:- In this test the patient lies flat on his back while the doctor lifts his leg up. If the patient experiences pain, it may be a sign of a herniated disc.
● Slump test:- This is also similar to the straight leg raise test, but the patient is asked to bend forward. This can help diagnose nerve root irritation or compression.
● Spinal Palpation:- In this test, the doctor will use his hands on the patient’s body to feel for abnormalities in the spine that may be causing pain.
● X-ray or MRI: Imaging tests in this test for low back pain can help identify any structural problems in the spine, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
● Laseg test:- In this the patient lies down on his back while the doctor lifts his leg and bends it at the knee.
Low Back Pain Medication
Low back pain can be treated with a variety of over-the-counter and prescription medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can reduce pain and swelling. Acetaminophen is an option for pain relief but does not reduce inflammation.
Muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine may be prescribed to reduce muscle spasms. In some cases, opioids may also be used for severe pain, but they carry a risk of dependence and other side effects. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider once before starting any medication for low back pain.
How it affect your daily life?
- Depression and Mood Swings
Constantly handling pain and therefore the stress of not knowing if the pain will improve can cause serious emotional issues. Depression, anger, anxiety and mood swings are just a few of the emotional side effects of chronic pain. While a bout of emotional pain is normal, if the problems persist, it’s time to try to something about it. attempt to distract yourself by doing activities you’re keen on if you’ll do so without pain.
- Low Self-Esteem
Chronic back pain can disrupt your life and make it harder to finish daily tasks and do the items you’re keen on . As a results of these limitations, sufferers often have diminished self-esteem. If you’re handling lowered self-esteem from chronic back pain, it’s important to undertake and alter your mindset directly . While it’s going to appear to be an uphill battle, understanding your worth is vital . Chronic back pain doesn’t define who you’re as an individual .
- Relationships
Many people underestimate what proportion chronic pain can affect relationships. As a result of pain and therefore the other emotional side effects that accompany chronic back pain, sufferers tend to become reclusive and recoil from social gatherings. Friends might not understand the physical and emotional turmoil those with chronic pain undergo, and successively, become distant. Family dynamics can change also. If chronic back pain is starting to affect your relationships, it’s time to speak to knowledgeable about pain-management or surgical options.
Cause of Lower and Upper Back Pain
Upper and middle back pain could also be caused by:
- More use of, muscle strain, or injury caused to the muscles, ligaments, and discs that support your spine.
- Poor posture.
- Pressure on the spinal nerves from certain problems, like a ruptured intervertebral disc .
- A fracture of 1 of the vertebrae.
- Osteoarthritis caused by the breakdown of cartilage that cushions the tiny facet joints within the spine.
- Myofascial pain that affects the animal tissue of a muscle or group of muscles.
- In rare cases, pain could also be caused by other problems, like gallbladder disease, cancer, or an infection.
Home Exercise for Backpain
It’s better to settle on a sort of exercise that you simply enjoy as you’re more likely to stay thereto . There are many sorts of exercise that have helped people with back pain. Examples include:
- swimming
- walking
- yoga
- Pilates
Many of the people that took part within the study also found that that they had the knowledge to stop further attacks if they felt an episode of back pain approaching .
Many community and sports centres also run yoga classes if you’re curious about trying it. confirm you speak to the yoga instructor before you begin so they’re aware that you simply have back pain.
You can find some samples of exercises you would possibly wish to attempt to reduce your pain on our exercises for the rear page.
You may feel some discomfort and sometimes pain once you exercise. this sense is normal and will settle down a couple of minutes after you finish. It’s not a symbol that you’re hurting yourself. Exercise will help reduce pain and may assist you manage your back pain better.
While you’ll push yourself and do strenuous exercise, it’s important to not overdo it. If you’re in pain that you simply can’t deal with during or after your activity, you’ll got to see a doctor. The key’s to start out off gently and to gradually increase the quantity you are doing .
Often people stop exercising once their back pain has cleared up. But if you stop exercising all the improvements you’ve made will disappear within a couple of weeks. So, it’s important that you simply still exercise regularly and don’t stop when the pain is gone and you’re feeling better.
low back pain ICD 10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases, a medical classification system used to code and classify diseases and health conditions. Low back pain is coded in the ICD-10 as M54.5.M54.5 refers to low back pain, which can be caused by a number of factors such as muscle strain, herniated disc, spinal stenosis, and osteoarthritis. The use of the specific ICD-10 code may depend on the underlying cause of the low back pain. Accurate coding of low back pain in the ICD-10 can help diagnose and diagnose this common health condition.
- M54.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to for reimbursement purposes.
- Low back pain ICD-10-CM M54.5 became effective on October 1, 2020.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M54.5 – other international versions of ICD-10 M54.5 may differ.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. Low back pain can be caused by a number of factors, including poor posture, muscle strains or sprains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, arthritis, osteoporosis, and spinal deformities. Other possible causes may include infection, tumors, and kidney stones. Further treatment options depend on the underlying cause and may include rest, physical therapy, medication, and surgery.
Ans. Low back pain can cause a variety of symptoms, some of the most important symptoms include dull or sharp pain, stiffness, muscle spasms, limited mobility, and pain radiating down the legs. In some cases, low back pain can also cause numbness or tingling in the legs or feet.
Conclusion:
Through today’s post, we have come to know what is Low Back Pain and what causes it. Apart from this, we have also understood about its symptoms. In conclusion, low back pain is a common and often debilitating condition that can be caused by a number of factors, from poor posture to underlying medical conditions. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the pain, and may include medication, physical therapy, or surgery. To prevent low back pain, it is important to maintain good posture, exercise regularly, and seek medical attention if pain persists. With proper care, most cases of low back pain can be effectively managed and alleviated.
Image Source- Google
Related Articles:
ICD-10 Codes in Medical Billing
ICD 10 Code for Abdominal Pain
The author and contributor of this blog "NSingh" is working in Medical Billing and Coding since 2010. He is MBA in marketing and Having vaste experience in different scopes of Medical Billing and Coding as AR-Follow-up, Payment Posting, Charge posting, Coding, etc.