GERD’s full name is Gastroesophageal reflux disease and it is a digestive disorder that occurs when the stomach acid backs up or refluxes into the esophagus. This condition is also called the acid-burning sensation of heartburn in the chest. Billing icd 10 for GERD needs correct coding of all the symptoms and treatments provided. Gerd ICD 10 is K21. 9 and all other related diagnosis codes are updated as well in below table.
Every person at one time or another is familiar with gastrointestinal troubles like acidity, indigestion, heartburn/GERD, bloating, diarrhea, gas, abdominal pain, cramps, constipation etc. These problems have become common among people today due to wrong and irregular eating habits. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation and chest pain. Sometimes, GERD can occur without esophagitis, which is inflammation of the esophagus. In these cases, patients may still experience symptoms of GERD but without noticeable damage to the esophagus.
According to the research of the American College of Gastroenterology about sixty million people in the USA experience acid reflux at least once a month. Approx. 15 million experience it every day. Due to this gastric disorder, serious complications like narrowing of the esophagus tube may occur.
Table of Contents
- ICD 10 for GERD:
- What is Gastro-esophageal reflux disease?
- How serious is Gastroesophageal reflux disease?
- How do you fix Gastroesophageal reflux disease?
- Does GERD go away?
- How to cure Gerd permanently?
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis symptoms
- How to Avoid GERD?
- CPT Codes for GERD:
- Conclusion:
- FAQs
- Related Articles:
ICD 10 for GERD:
We used ICD 10 for GERD is K21.9, It is a billable ICD-10-CM code and is also used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Other Gerd ICD 10 codes are as mentioned below
| ICD Codes | Description |
| K20.8 | Other esophagitis |
| K20.80 | ICD codes for without bleeding |
| K20.81 | with bleeding |
| K20.9 | Esophagitis, nonspecified |
| K20.90 | Without bleeding |
| K20.91 | With bleeding |
| K21 | Gastro-esophageal reflux disease |
| K21.0 | Gastro-esophageal reflux disease with esophagitis |
| K21.00 | Without bleeding |
| K21.01 | With bleeding |
| K21.9 | Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis |
| K22 | Other diseases of esophagus |
| K22.0 | Achalasia of cardia |
| K22.1 | Ulcer of esophagus |
| K22.10 | Without bleeding |
| K22.11 | With bleeding |
| K22.2 | Esophageal obstruction |
| K22.3 | Perforation of esophagus |
| K22.4 | Dyskinesia of esophagus |
| K22.5 | Diverticulum of esophagus acquired |
| K22.6 | Gastro-esophageal laceration-hemorrhage syndrome |
What is Gastro-esophageal reflux disease?
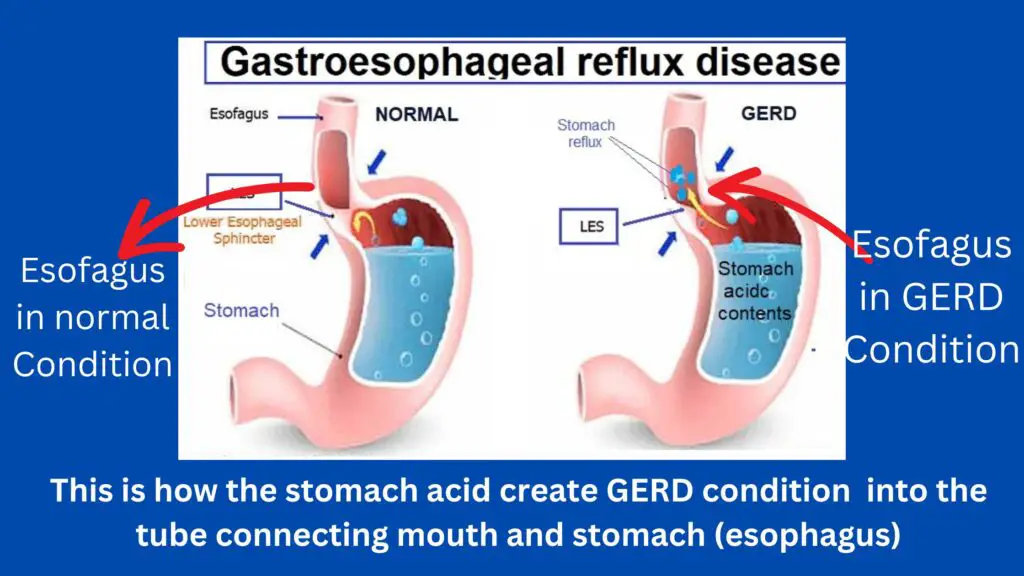
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter, the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis causes stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, causing underlying physical disorders such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain.

GERD can lead to more serious complications and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, avoiding triggers such as fatty or spicy foods, and not eating before bedtime, can help sufferers manage GERD.
How serious is Gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic health condition in which stomach acid and partially digested food flow back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and damage to the esophagus. It is considered a serious condition because if Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis is left untreated, it is capable of leading to serious complications like esophagitis, stricture, Barrett’s esophagus and in some rare cases, cancer of the esophagus .
GERD can also negatively affect a person’s quality of life, causing symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and a persistent cough. In some cases, GERD can cause sleep disturbances, and can affect daily activities and also cause anxiety or depression. If you are experiencing symptoms of GERD, it is important to see a doctor in this situation. In severe cases, Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis Surgery may be needed to treat and prevent further complications.
How do you fix Gastroesophageal reflux disease?
To fix gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis, follow the following steps:-
● Lifestyle Changes:- Avoid trigger foods like spicy, acidic or fatty foods. In addition, quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and maintain a healthy weight.
● Medicines: Over:- The-counter antacids can help neutralize stomach acid. Your doctor may also prescribe stronger medications, such as H2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors, to reduce the production of stomach acid.
● Keep the head of the bed elevated: This helps reduce the symptoms of acid reflux by preventing stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus.
● Avoid large meals at one go :- Eating large meals can increase the amount of pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter, which can lead to reflux. Eating smaller, more frequent meals may help reduce symptoms.
● Take a short walk after eating:- After eating, wait at least three hours before lying down or going to bed and must take a short walk.
Does GERD go away?
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis is a chronic condition that is usually managed rather than cured. Some people may experience spontaneous remission of symptoms, but for most people, GERD is a lifelong condition that may require ongoing management.
Treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and losing weight, and medications, such as antacids or proton pump inhibitors. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct underlying physical problems that contribute to Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (Gerd) . With proper treatment and management, most people with GERD are able to control their symptoms and lead normal, healthy lives.
How to cure Gerd permanently?
To cure Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) completely forever, we have to change these elements in our life:-
●Change your diet: Eating spicy, acidic, or high-fat foods can bad Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis
symptoms. Instead, focus on eating healthy, whole foods such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and low-fat dairy products. Additionally, consider eating smaller meals more often throughout the day instead of large, heavy meals.
●Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight can put extra strain on your stomach and contribute to GERD symptoms. Losing weight, if needed, and maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a healthy diet may improve your symptoms.
●Manage stress: Stress can cause an increase in acid production, which leads to symptoms of GERD. Incorporating stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation or yoga into your daily routine may help reduce stress and improve your symptoms. Additionally, avoiding stress-causing factors such as caffeine, alcohol, or tobacco may also help reduce GERD symptoms.
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease with esophagitis without bleeding
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid and digestive juices back up into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation known as esophagitis. When there is no bleeding, it is called “non-erosive” GERD. Symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and trouble swallowing.
Gastro esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis symptoms
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition where stomach acid and partially digested food flow back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and damage to the tissue. Some of the most common symptoms of Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis include:-
Heartburn:- There is a severe burning sensation in the chest during GERD, which often worsens after eating.
Regurgitation:- A feeling of acid or partially digested food coming back into the mouth. Its taste is mind-boggling and sometimes sour.
Chest pain:- A feeling of pressure in the chest that can be mistaken for a heart attack.
Dry cough:- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis is a persistent cough that is not caused by a respiratory infection.
Sore throat:- Persistent sore throat that is not caused by cold or flu.
How to Avoid GERD?
A healthy diet and a positive lifestyle can help to reduce the frequency of acid reflux GERD. The most common reason is heartburn or a burning sensation in the chest, usually after eating. Some of the common symptoms like chest pain, regurgitation of food or sour liquid, difficulty swallowing, nausea or vomiting, and a sensation of a lump in your throat, etc.
So need to follow a healthy routine and add some physical exercise in daily life for better digestion, and not to collect unhealthy fat in the body. Some meditation and yoga also help to reduce heartburn.
There are some points that need to maintain
- Do not smoke.
- Don’t lie down just after a meal, walk at least 800 steps after the meal.
- Eat food slowly and chew thoroughly. …
- Avoid junk foods and soft drinks
- Avoid uncomfortable clothes
CPT Codes for GERD:
| CPT Codes | Description |
| 43200 | Esophagoscopy, diagnostic |
| 43201 | Esophagoscopy flexible, transoral; with directed submucosal injections, any substance |
| 43210 | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, flexible, transoral, with esophagogastric fundoplasty, partial or complete, includes duodenoscopy when performed |
| 43236 | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, flexible, transoral; with directed submucosal injection(s), any substance |
| 43241 | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, flexible, transoral; with insertion of intraluminal tube or catheter |
| 43257 | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, flexible, transoral; with the delivery of thermal energy to the muscle of lower esophageal sphincter and/or gastric cardia, for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| 43284 | Laparoscopy, surgical, esophageal sphincter augmentation procedure, placement of sphincter augmentation device (i.e., magnetic band), including cruroplasty when performed |
| 43289 | Nonlisted laparoscopy procedure, esophagus |
| 43499 | The nonlisted procedure, esophagus |
| 43999 | Non-listed procedure, stomach |
Conclusion:
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) without esophagitis is a type of disorder that arises due to acid and partially digested food. Through today’s post, we have come to know what is Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD), what are its symptoms and what could be the reasons for it. Apart from this, we also learned how we can protect ourselves from it.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition where stomach acid regularly backs up into the esophagus, causing heartburn and other symptoms. If no evidence of esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus) is present, the condition is called non-erosive GERD.
We have also discussed this topic in this article. If you still have any confusion related to Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis, then you can ask us in the comment box. However, it is important to speak to a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan, as untreated GERD can lead to serious complications.
FAQs
Ans. Non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a health condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation, but without causing damage or erosion of the esophagus. This is an acute form of GERD.
Ans. Avoid triggers like fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine and alcohol.
● Instead of taking big food, take small food.
● Raise the head of your bed.
● Eat 2 hours before sleeping.
● Chewing can be done to increase saliva production.
● Exercise regularly every day.
Ans. Acid reflux is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and other symptoms. Some people find relief from symptoms by changing their diet and drinking habits. Here are some drinks that help neutralize the acid.
water.
Aloe vera juice.
Ginger tea.
Green tea.
Herbal tea
.
Reference Articles–
Image Source- Google
Related Articles:
The author and contributor of this blog "NSingh" is working in Medical Billing and Coding since 2010. He is MBA in marketing and Having vaste experience in different scopes of Medical Billing and Coding as AR-Follow-up, Payment Posting, Charge posting, Coding, etc.

