ICD 10 Code for Dysphagia is R31.10 . Dysphagia is a complex disorder primarily caused by neurological damage or disease. It can cause many physical and emotional problems which affect the overall quality of life of the patient. Symptoms of dysphagia include difficulty with oral intake, abnormal breathing patterns when swallowing, recurrent chest infections, coughing and choking during feeding, changes in vocalization during swallowing attempts, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
With early detection and accurate diagnosis, the condition can be managed with specific strategies such as dietary modification protocols or food texture modifications to make food easier to swallow. Appropriate precautionary measures will also need to be taken to prevent cravings and ensure proper nutrition. In addition to medical treatment, occupational and speech therapy may also be used to help circumvent the limitations associated with dysphagia.
Table of Contents
- ICD-10 Code for Dysphagia
- Causes of Dysphagia
- Symptoms of Dysphagia
- Effects of Dysphagia on body
- How to Protect ourself from dysphagia ?
- FAQs
- Conclusion:
- Related Articles:
ICD-10 Code for Dysphagia
ICD10 Codes for Dysphagia and other related diseases with dysphagia is mentioned in table as below.
| Description | ICD Codes |
| Without nausea | R11.11 |
| Projectile vomiting | R11.12 |
| Fecal matter | R11.13 |
| Bilious vomiting | R11.14 |
| Cyclical vomiting syndrome unrelated to migraine | R11.15 |
| Nausea with vomiting, unspecified | R11.2 |
| Heartburn | R12 |
| Aphagia and dysphagia | R13 |
| Aphagia | R13.0 |
| Dysphagia | R13.1 |
| Dysphagia Unspecified | R13.10 |
| Oral phase | R13.11 |
| Oropharyngeal phase | R13.12 |
| Pharyngeal phase | R13.13 |
| Pharyngoesophageal phase | R13.14 |
| Other dysphagia | R13.19 |
| Flatulence and related conditions | R14 |
| Abdominal distension (gaseous) | R14.0 |
| Gas pain | R14.1 |
| Eructation | R14.2 |
| Flatulence | R14.3 |
Causes of Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a disorder of swallowing, which can be caused by a number of physical or neurological factors. In this, one has to face extreme difficulties in swallowing food while eating any thing or food. Some of the reasons for this are as follows-
◆Poor control of the muscles responsible for the process of swallowing and gastroesophageal reflux are two common causes.
◆ Additionally, certain medical conditions may also be responsible for dysphagia such as stroke, head and neck cancer, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis and motor neurone disease.
◆ Dysphagia can also result from an anatomical defect such as a blockage or stricture in the pharynx or esophagus.
◆Also, trauma to the mouth or throat can cause dysphagia.
◆ Reaction to medications may be responsible for dysphagia.
◆ Toxins that can affect nerve and muscle functions.
◆ Poor nutrition.
◆ Dehydration resulting from difficulty in swallowing fluids.
◆ Behavioral issues associated with dementia and Alzheimer’s disease
◆ Specific diseases like muscular dystrophy.
Symptoms of Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a swallowing disorder that affects the ability to swallow solid, liquid and/or semi-solid foods. It can be indicated by a variety of symptoms, some of the symptoms of dysphagia are as follows-
◆ Coughing or choking when trying to swallow.
◆ Moist or gurgling sounds when swallowing.
◆ Includes difficulty breathing and chest pain after eating due to food entering the airways instead of the esophagus.
◆ Regurgitation of food and liquids among other symptoms of dysphagia.
◆Frequent heartburn or sore throat after eating.
◆Difficulties in eating include weight loss and inability to tolerate textures other than very soft foods.
Effects of Dysphagia on body
Dysphagia can have significant effects on the body.
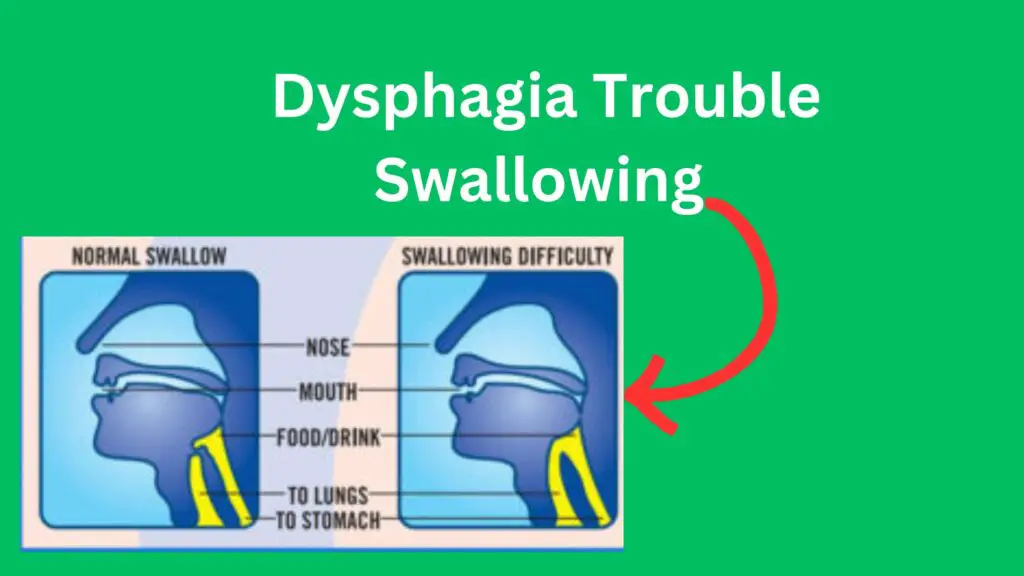
◆This can lead to malnutrition, dehydration and weight loss due to reduced food intake.
◆ Dysphagia can lead to a risk of aspiration and pneumonia as well as decreased pulmonary and general health due to nutritional immune system deficiencies.
◆Difficulty swallowing often causes tension which can lead to increased heart rate, fatigue and anxiety.
◆ People with dysphagia may become socially isolated because the consequences of eating are difficult or impossible.
◆It further aggravates nutritional deficiencies and associated diseases leading to malnutrition.
◆ Inadequate nutrition due to dysphagia also increases the risk of pressure sores secondary to immobility.
◆ It also leads to deep vein thrombosis due to decreased mobility.
How to Protect ourself from dysphagia ?
To protect themselves from dysphagia, a person should be aware of the possible causes and risk factors associated with their condition, as well as their symptoms. It is important for sufferers to maintain adequate levels of hydration, and those who have difficulty swallowing should avoid consuming hard or crunchy foods, which may require more effort as they move down the throat. Additionally, pausing during a meal can give your body more time to swallow. One should also pay attention to how quickly they consume food, avoiding any large bites that could go down the wrong pipe and cause irritation in the throat or chest. Finally, it is important to seek medical intervention if necessary.
FAQs
Ans. Dysphagia can lead to malnutrition due to inadequate intake of nutrients as a result of the inability to swallow normally. To manage these issues, it is important for individuals with dysphagia to consult with their healthcare provider for an evaluation and possible treatment options.
Ans. Following are the four stages of dysphagia-
1. Oral preparation
2. Verbal promotion
3. Pharynx
4. Esophagus
Conclusion:
Dysphagia is a rare seen health problem which is seen in very few people. But it can be extremely painful as it can lead to many problems while swallowing food which is definitely a matter of concern. But we have explained in detail how dysphagia can be avoided and what are its symptoms and causes. However, treatment for dysphagia must be individualized based on each patient’s diagnosis. And it is also essential that individuals with dysphagia consult a health care professional for proper evaluation, management, and long-term monitoring of their condition.
Image Source- Google

